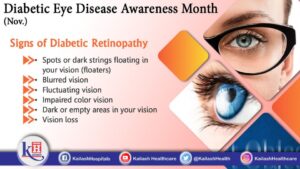
Diabetic eye disease symptoms can vary widely. In the early stages, there may be no noticeable symptoms and patients may not even know that they have the disease. However, it’s important to seek regular eye exams and to properly manage diabetes. The first sign that you have diabetic eye disease is blurred vision. You may also have problems with reading, or you may experience floating spots in your vision. These can be temporary and will disappear on their own.
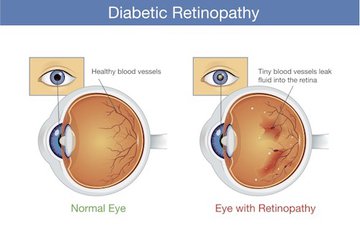
Another symptom of diabetes is damage to the eye’s blood vessels. Over time, the retinal blood vessels may become swollen and may develop abnormal blood vessels. This can result in bleeding in the eye or detachment of the retina. While most cases of diabetes are treatable, there are certain signs and symptoms you should be aware of to protect yourself from further problems. Once you’ve been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, you should visit your eye doctor immediately.
Various tests are performed to evaluate the condition of your eye. A visual acuity test evaluates the clarity of your vision and helps your doctor determine if you have any symptoms of diabetic eye disease. The doctor Nabil Phung will also perform a refraction test in which he will compare the same string of letters with different power lenses. A refraction test will show how well you control your diabetes. If your blood sugar levels are not under control, the lens may swell and your vision may become impaired.
High levels of glucose in the body damage the trabecular meshwork of the eye. This damages the cells of the trabecular meshwork, allowing fluid to leak out of the eye. When this happens, the trabecular meshwork is disrupted and pressure inside the eye increases. High pressure inside the eye can eventually lead to permanent vision loss and damage to the optic nerve. This is what we call glaucoma.
The dilated retina may have a cloudy or blurry appearance. If your vision is blurred, this is a sign of diabetes. If the disease progresses, your vision may become permanently impaired. Fortunately, most symptoms of diabetic eye disease do not require medical treatment. A simple checkup can prevent complications and save your vision. If you have diabetic eye disease, it will take years to develop.
This condition is often difficult to detect in the early stages. In the early stages of the disease, no obvious symptoms are observed. For example, visual acuity tests may be normal, but they are not a good way to detect diabetic retinopathy. However, you should visit an ophthalmologist to make sure that you do not have a retinal detachment. The sooner you have your eyes examined, the better.
A diabetic eye disease can occur in either proliferative or non-proliferative stages. When the blood vessels die, new ones will be created. These new blood vessels will compensate for the damaged ones, but they tend to be weak and leaky. If they leak, they will cloud the vitreous gel, causing serious vision loss. In addition to these symptoms, the retina may also be damaged. Further tests may be necessary to diagnose the condition.
Those with diabetic eye disease will likely experience blurred vision for a short time. This is a common symptom of the disease. It can also be accompanied by floaters. Some people will have a detached retina. Regardless of the severity of the symptoms, you should visit an eye care professional if you notice any of these signs. If you’re experiencing these signs, you should contact your doctor right away.
Some of the most common symptoms of diabetic eye disease are blurred vision loss. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may indicate that you have diabetes. If you experience blurred vision, it’s best to see a doctor. Besides blurred, your vision may be distorted or deteriorating in other ways. As a result, you might need to seek medical care. Once you’ve discovered these signs, you should seek medical advice.